Stuart Hall – Encoding, Decoding

Roland Barth a French philosopher argues that myth contains ideological meanings.Myth and ideology in their structuralist senses are synonymous.
Louis Althusser a French philosopher
Agrues that individual in capitalist societies are governed by ideological state apparatuses (Isas)
Including schools, legal systems, religious institutions, media communication and so on and on
The approach to Marxism
More sophisticated than the classical Marist notion of top-down false conscious which suggests that ideology is imposed from above by elite powers upon the unknown masses.
ISAS points to a more linguistic or discursive conception of ideology (hall 1996 a:30) that is reproduced by various institutional practices and structures.
Ideology by Stuart Hall
Hall definition: ideas, meaning, conceptions, theories, beliefs etc. And the form of consciousness which are appropriate to them (Hall 1977.320)
Effects mode of communication
Models of effect such as lass-well formula theorize the communication process in terms of reliability. If messages are not received as intended, this is deemed a failure of technical communication. According to effects perspectives messages are not received correctly if the channel of communication from the sender to recipient are distoreted by electrical or human error. The meaning of messages themselves are assumed to be distortion –free and universal transferable.
Effect models are flawed because they fail to situate media communications within existence social, economic, and political structures. The meaning of the messages. Then can be distorted and interpreted differently than intended according to the positions of producers (senders) and audiences (recipients) within these existing structures. Meaning is a social production, a practice. The world must be made to mean. Language which had sustained previous content analysis, where the meaning of a particular term or sentence could be validated simply by looking at what in the real world, it referenced ( Hall 1982: 67)
Hall argues on the way the the model of communication.
To understand the sense-making process by which media transmit messages to their audiences.
Language is encoded by those with the means of meaning production and is then decoded by audience ( Hall 1982:68)
Hall extends the semiotic theory of meaning construction to a model of media production and reception, commonly known as the encoding/ decoding model of communication.
Encoding /decoding the codes of encoding and decoding may not be a perfect symmetrical
Hall also interested in how media represent and misrepresent by what they mean rather than simply reflect those meaning on their audiences
Encoding and decoding Model
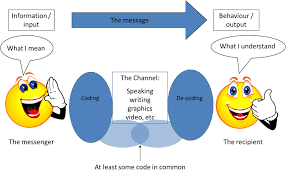
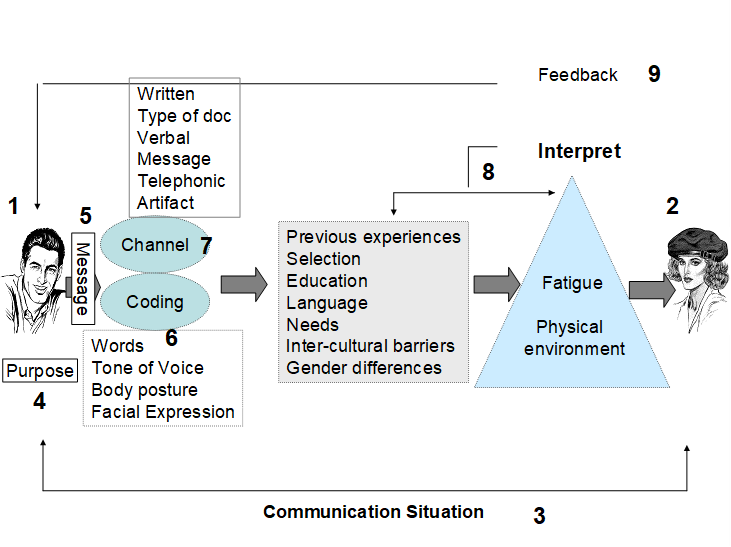
Media production operate within a set of professional codes such as technical competence and high –budget production values.
These professional codes generate preferred meanings that have the institutional /political /ideological order imprinted in them and have themselves become institutionalized.
In a determinate moment the structure employs a code and yields a message at another determinate moment the message via the decoding, issues into the structure of social practice.
Media as a language Systems
Structured through a set of rules, codes and values that make them highly prone to ideological constructions of meaning or what Barthes refers to as myths.
Television is primary myth-maker constructer of ideology –according to Hall
Decoding
An audience member may adopt a dominant code which accepts the preferred meaning intended by the encoders (Media producers)
An audience member adopts a negotiated code which accepts some preferred meaning of media producers, in which case they adopt an oppositional code and decode the message in a global contra way.
The purpose of encoding and decoding
An attempt to rediscover and rescue ideology from its conception as an omnipotent,oppressive force wielded by the ruling classes upon the masses in the classical Marxist traditional of political economy theory.
References:
Hall.S (1980) Encoding/decoding in .S. Hall, D. Hobson, A. Lowe, and P. Willis (ed) Culture, Media language: working papers in cultural studies 1972-79. London: Hutchinson: 128-38
Hall, S (19785) television as a medium and its relation to culture CCS Stenciled paper No 34 Birmingham: University of Birmingham
Hall, S 91977) Culture, the media, and the ideological effect in J. Carran, Gurevitch and J Woollacott (eds) Mass Communication and society. London: Arnold 315-48
.

